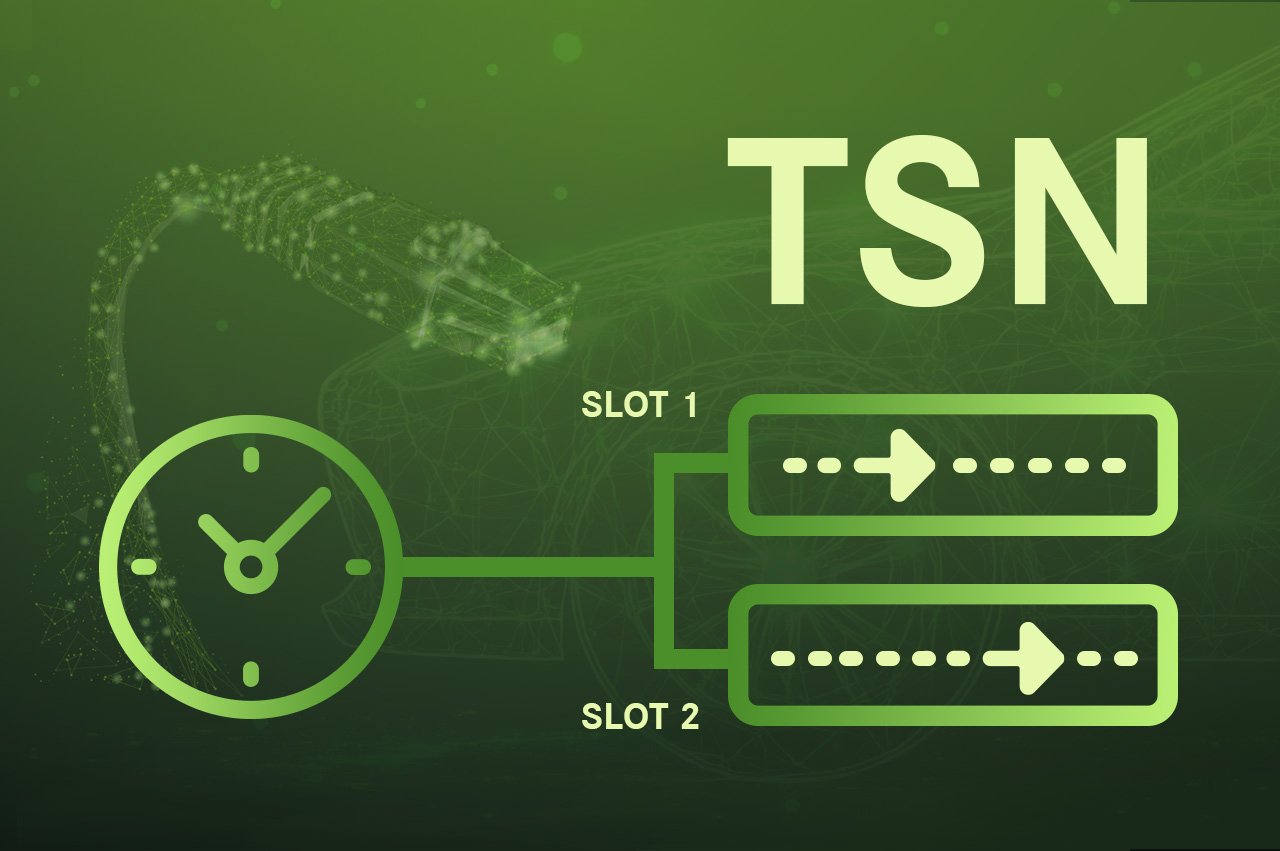
What is TSN and why is it critical?
Why Ethernet as a Foundation?
The main TSN Standards you need to know
TSN in Automotive Applications
TSN and the OSI Model
Challenges and Considerations
How STAR ELECTRONICS can help
Key Takeaway
Glossary